11 Guides to Protect Company Data from Malware Attack

Malware effects into company can destroy data. It can be through ransomware, theft of data, or a software vulnerability that is exploited by hackers. Data destruction may occur when the malware takes over a computer and encrypts files, making them inaccessible. If the data is critical to the company’s operations, it may be difficult to restore. In some cases, the malware can spread to other computers in the organization, resulting in even more damage.

Define malware & Its development
Malware, or malicious software, is software that can cause damage to a computer. It can be developed by anyone, including individuals and groups with malicious intent. Malware often hides itself from normal detection mechanisms, making it difficult to remove without proper tools.
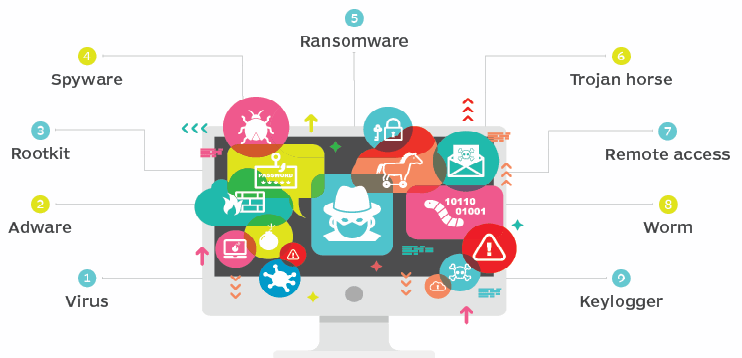
Malware can be categorized by its purpose: destructive malware seeks to delete data or damage systems; spyware gathers information about the user; and ransomware encrypts files and demands payment in order for users to access them again. Malicious code can also be disguised as legitimate applications, making it more difficult for users to identify and avoid infection. Malware development has become increasingly complex over the years due to the increasing number of varieties of malware and the corresponding number of ways in which they can spread.
What malware can do?
Malware can do a lot of different things. It can steal your data, encrypt your files, and even take over your computer. But there are also a few types of malware that can do more subtle things, like tracking your online activities or spying on you. Here are some of the most common ways malware can impact your computer:
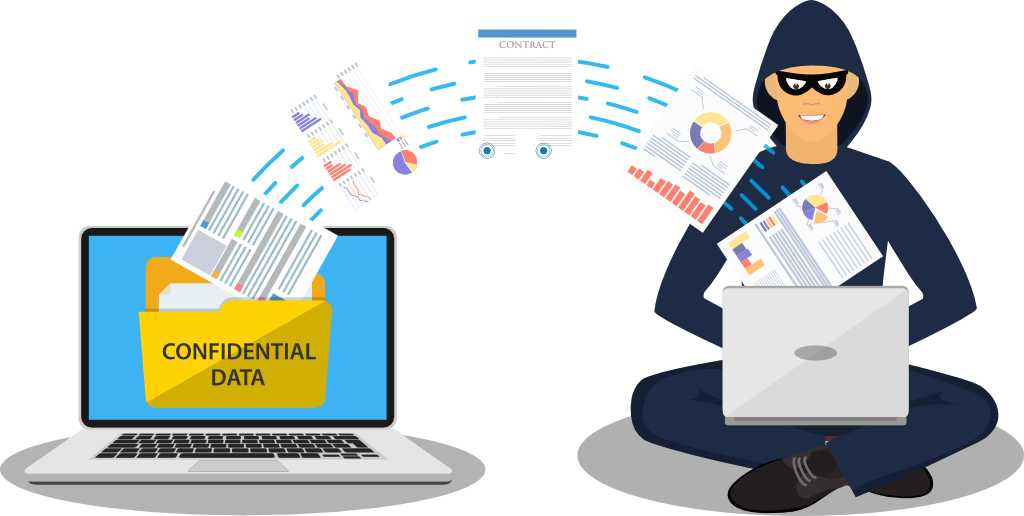
-Stolen Data: Malware can steal your data, including passwords, bank information, and personal photos.
-Encryption: encrypt your files so that you cannot access them or delete them.
-Computer Takeovers: Malware can take over your computer completely, preventing you from using it or accessing important files.
-Online Tracking: track your online activities and send the information to whoever created the malware.
How does malware affect a company?
Malware is a type of malicious software that can affect a company in a variety of ways. It can steal sensitive data, disable security features, and even carry out attacks on other systems. Have a negative impact on both the bottom line and the overall health of a company. Here are some ways malware affects companies:

It steals confidential information: One of the most common ways malware affects companies is by stealing confidential data. This could include user passwords, financial data, or trade secrets.
It damages systems: Malware can also damage systems by disabling security features or carrying out destructive attacks on other systems. This can result in lost income or damage to customer relationships.
It increases costs: Malware also often increases costs by forcing companies to replace damaged equipment or upgrade security measures. In some cases, it can even lead to business disruption.
How Does It Steal Information and Destroy Computer?
Malware can trick you into downloading it, or it can come attached with a file you want to download. Once installed, malware will begin tracking your online activities, collecting information such as passwords and account numbers. It will then send this information back to the malware author for use in future attacks. It often uses techniques to hide itself from the user, so it is hard to know when it is active on a computer. Malware can run in the background or popup unexpectedly, causing users to lose important information or files.

Once installed, malware can monitor what users do on their computers, collecting passwords and other confidential information. It can also take advantage of security flaws in programs to gain access to files or networks. This stolen data can be used to help spread the malware further, or it can be sold on the black market to other malicious actors. It is growing more sophisticated all the time, and it’s becoming increasingly difficult for users to protect themselves from its attacks.
How do companies lose electronic data?
Companies are increasingly becoming victims of malware, which is a type of computer virus. Malware can infect a company’s computer systems and steal confidential information, including e-mails, files, and passwords. The data loss can be costly for companies, as it can result in lost profits and customers. There are several ways that companies can lose electronic data due to malware: by losing access to files; by being infected with malware and having the data stolen; or by being forced to pay money to hackers in order to regain access to their data. Companies need to be vigilant about the security of their computers and take steps to prevent the loss of electronic data.
Virus-Malware, or computer viruses, can wreak havoc on a company’s electronic data by deleting files, altering data, or spreading across a network. In order to prevent such damage and ensure the safety of their information, companies must be proactive in protecting their systems against malware. There are several steps that companies can take to protect themselves from malware infection: regularly update software and firmware; keep systems patched; use firewalls and intrusion detection/prevention systems; use secure coding practices; and institute a policy of minimum access privileges. By taking these measures, companies can reduce the chances of losing valuable data due to malware.
11 possible causes of data loss?
There are many possible causes of data loss. These can include accidental deletion, ransomware attacks, improper storage and transmission of data, and malicious actions by third-party hackers. In some cases, data loss may be caused by human error or malfunctioning equipment. Regardless of the cause, timely detection and addressing of data loss can help minimize its impact on business operations. Here are the 11 possible causes of data loss.

1. There are a variety of possible causes for data loss, ranging from accidental deletion to hacking.
2. Poor storage and protection of data can lead to its loss or theft.
3. Failure to properly back up data can lead to its loss in the event of a computer crash.
4. Infections and viruses can corrupt or damage files, leading to their loss or theft.
5. Accidental alteration or deletion of important data can also cause its loss.
6. Unsuspected power outages, hardware failures, and human error can all lead to the loss of data as well.
7. Human Error: A user might lose data due to their own mistakes, such as typing the wrong password or deleting files without backup.
8. Natural Disasters: Earthquakes, floods and other natural disasters can damage or destroy electronic equipment, leading to lost data.
9. System corruption: A system’s files can become corrupted if the computer is infected with a virus or if there is an error in the operating system. In order to restore corrupted files, you’ll need to restore the system from its backup copy.
10. Software misconfiguration – Incorrect settings on computer systems or applications may result in lost data.
11. Incompatibilities: If you try to save a file that was created in an earlier version of a program, the file may not be compatible with the new version and may result in data loss.
Malware causes data destruction?
The recent increase in malware infections has caused data destruction and business interruption. This can be due to ransomware, a type of malware that encrypts files on the user’s computer and demands a ransom payment before the data can be restored. In other cases, malware may delete or change critical files, preventing users from accessing their data or making it inaccessible. Malwarebytes’ Anti-Malware diagnostic tool detects and removes malware from your computer, helping to prevent data destruction.
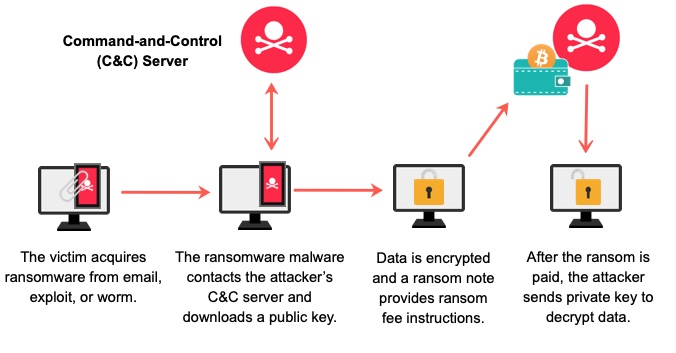
In some cases, the malware destroys data that is essential to running the business, such as financial records or customer information. In other cases, the malware can just cause system slowdown or inconvenience. No matter what the end result, it’s important to know how to identify and prevent malware from causing data destruction.
How hackers and viruses can harm the organizations?
Viruses and hackers can have a negative effect on organizations by damaging data, disrupting operations, and even costing companies money. Viruses and hackers can enter an organization through various means, such as email or file sharing. Once inside, they can spread quickly through networks of employees. Viruses and hackers can also be created intentionally to damage or destroy an organization’s software or data.

Organizations should take steps to protect themselves from viruses and hackers. They should use anti-virus software to detect and prevent infections. They should also keep up-to-date with the latest security patches from software providers. Organizations can also train their employees about how to avoid becoming infected with viruses and how to report suspicious activity. In addition, organizations should take measures to protect their data from being stolen or destroyed by viruses or hackers.
How do companies protect against malware?
Computer viruses, are a growing problem for businesses of all sizes. In order to protect their computers and data from malware, many companies use antivirus software and other security measures. However, malware can still get onto a company’s systems through various means, such as email attachments or downloads from untrustworthy sources. Here are some ways to protect against malware:

1. Use a reliable antivirus software program: Antivirus programs help to detect and remove malware from your computer system. Make sure that the program you choose is up-to-date and has been tested for compatibility with your computer system.
2. Keep your computer system clean: Keep your computer systems clean by using a virus scanner on a regular basis to check for and remove any malware that may be lurking on your system.
3. Educate your employees on the dangers of malware. Make sure they understand the signs of infection and how to avoid downloading or opening suspicious attachments or links.
4. Keep up with industry-leading security solutions. Many security solutions offer features that can help protect your business against malware attacks.
5. Use strong passwords and keep them confidential. Make sure all users are using unique, complex passwords that are not easily guessed or stolen by unauthorized individuals. Store passwords in a secure location away from prying eyes.
FAQs
How is malware a threat to data?
Virus is a threat to data because it can corrupt or destroy files and data. It can infect computers through email, websites, or downloads. Once installed, malware can spread through networks and affect other computers. Corrupted Virus can also spread without users knowing about it, using methods such as viruses and worms.
What are the reasons for malware attacks?
Virus attacks are on the rise, and there are numerous reasons why this is so. Here are three of the most common:
1. Financial gain: Malware creators seek to make money by stealing data or infecting victims’ computers with malware that can then be used to generate profits.
2. Politics and revenge: Developers sometimes use malware as a tool for political or revenge motives, attacking opponents or anyone whose views they oppose.
3. Fear and intimidation: Many people are afraid of cybercrime, which can lead them to inadvertently install malicious software on their devices without realizing it.
Conclusions:
In conclusion, malware effects into companies in a variety of ways, and can destroy data if not detected and treated. Educating employees on the dangers of malware and how to protect themselves is essential to keeping their data safe. Taking steps such as regularly backing up data, installing anti-virus software, and using strong passwords are also important. Finally, businesses should always be prepared to respond to an attack by taking measures such as creating a response plan and having an incident response team in place. Try MalwareBytes.